ABOUT

Takafumi Tsukui
I am a Postdoctoral Fellow at Kavli IPMU, the University of Tokyo. You can read more about me in the RSAA newsletter.
I did my PhD at Graduate University for Advanced Studies, SOKENDAI and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. You can find my PhD thesis here titled "Formation and Evolution of Galactic Structures Using Gas and Stellar Kinematics".
I obtained my Bachelor in Physics at Tohoku University (Japan).
Research
Galaxy formation and evolution
I am interested in how galaxies have formed and evolved across cosmic time. The motion of star and gas within galaxies give us clues about how galaxies have evolved, how massive they are, and how galaxies will evolve.
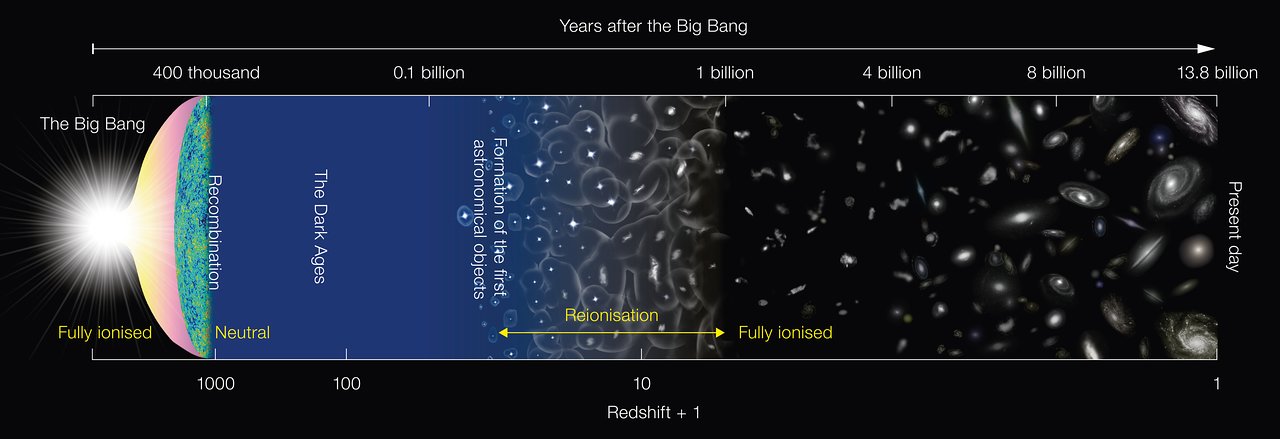 Schematic diagram of the history of the Universe, Credit NAOJ
Schematic diagram of the history of the Universe, Credit NAOJ
My research focus is to elucidate the structure of galaxies from the early Universe to the current Universe, analysing gas and stellar kinematics measured by state-of-the-art telescopes such as the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
Fundamental Measurement Method
Signals from galaxies are extremely faint and can be overwhelmed by noise sources, such as radiation from Earth's atmosphere and thermal fluctuations of observation instruments. Therefore, a crucial aspect of research involves determining the probability of random noise mimicking a signal.
The astronomical images obtained through so-called interferometric observations exhibit complex correlation patterns that vary from one observation to another. Tsukui et al. 2023 address the fundamental understanding of the correlated noise in the image and propose flexible methods to assess the uncertainty of scientific results. Read more.
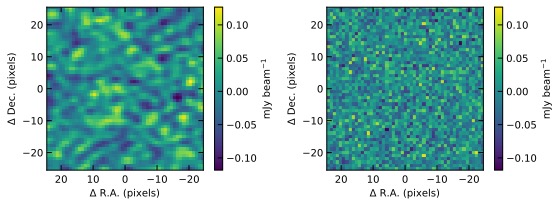 Generated pseudo-noise images: one with pixel correlation (left), and the other without (right). Both have the same level of random fluctuation, but their visual appearances differ significantly, leading to distinct impacts on the uncertainty of scientific results. Credit: T.Tsukui
Generated pseudo-noise images: one with pixel correlation (left), and the other without (right). Both have the same level of random fluctuation, but their visual appearances differ significantly, leading to distinct impacts on the uncertainty of scientific results. Credit: T.Tsukui
Publications
Link to Google scholar / Link to academic presentations
First author
- T. Tsukui, E. Wisnioski, J. Bland-Hawthorn, K. Freeman 2025, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 540, "The emergence of galactic thin and thick discs across cosmic history"
NASA/ADS
- T. Tsukui, E. Wisnioski, J. Bland-Hawthorn, Y. Mai et al. 2024, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 527, "Detecting a disk bending wave in a barred-spiral galaxy at redshift 4.4"
NASA/ADS
- T. Tsukui, E. Wisnioski, M. R. Krumholz, A. Battisti 2023, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 523, "Spatially resolved dust properties and quasar-galaxy decomposition of a hyper-luminous infrared galaxy at z=4.4"
NASA/ADS
- T. Tsukui, S. Iguchi, I. Mitsuhashi, and K. Tadaki 2023, Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems, Vol. 9, "Estimating the statistical uncertainty due to spatially correlated noise in interferometric images"
NASA/ADS
- T. Tsukui, and S. Iguchi 2021, Science, Vol. 372, "Spiral morphology in an intensely star-forming disk galaxy more than 12 billion years ago"
Free access to the article / NASA/ADS
Co-author
- R. Ikeda, D. Iono et al. (incl. T.Tsukui), The Astrophysical Journal, "Formation Of Sub-Structure In Luminous Submillimeter galaxies (FOSSILS): Evidence of Multiple Pathways to Trigger Starbursts in Luminous Submillimeter Galaxies"
NASA/ADS
- I. Kanowski, E. Wisnioski, T. Mendel, A. Marchal, T.Tsukui 2025, Royal Astronomical Society Techniques and Instruments, "Spatially non-parametric recovery of intrinsic kinematic maps in pre- to post-merger galaxies"
NASA/ADS
- E. Wisnioski, T. Mendel, R. Leaman, T.Tsukui et al. 2025, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, "Evolution of Gas Velocity Dispersion in Discs from z ~ 8 to z ~ 0.5"
NASA/ADS
- K. Tadaki, F. Esposito, L. Vallini, T.Tsukui et al. 2025, Nature Astronomy, "Warm gas in the vicinity of a supermassive black hole 13 billion years ago"
Free access to the article/NASA/ADS
- J. Bland-Hawthorn, T. Tepper-Garcia, O. Agertz, (incl. T. Tsukui) 2025, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, "Turbulent gas-rich discs at high redshift: origin of thick stellar discs through 3D 'baryon sloshing'"
NASA/ADS
- T. Bakx, A. Amvrosiadis, G. Bendo et al. (incl. T. Tsukui) 2024, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 535, "A novel high-z submm galaxy efficient line survey in ALMA Bands 3 through 8 - an ANGELS pilot"
NASA/ADS
- G. Santucci, C. Lagos, K. Harborne et al. (incl. T. Tsukui) 2024, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 534, "The MAGPI survey: orbital distributions, intrinsic shapes, and mass profiles for MAGPI-like EAGLE galaxies using Schwarzschild dynamical models"
NASA/ADS
- Y. Mai, S. Croom, E. Wisnioski et al. (incl. T. Tsukui) 2024, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 533, "The MAGPI Survey: the evolution and drivers of gas turbulence in intermediate-redshift galaxies"
NASA/ADS
- Q. Chen, K. Grasha, A. Battisti et al. (incl. T. Tsukui) 2024, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 527, "The MAGPI survey: effects of spiral arms on different tracers of the interstellar medium and stellar populations at z 0.3"
NASA/ADS
- L. Maud, Y. Asaki, H. Nagai, T. Tsukui, et al. 2023, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, Vol. 267, "ALMA High-frequency Long-baseline Campaign in 2019: Band 9 and 10 In-band and Band-to-band Observations Using ALMA's Longest Baselines"
NASA/ADS
- R. Ikeda, T. Morishita, T. Tsukui, et al. 2023, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 523, "Near-infrared characterization of ultra-diffuse galaxies in Abell 2744 by JWST/NIRISS imaging"
NASA/ADS
- D. D. Nguyen, M. Bureau, S. Thater et al. (incl. T. Tsukui) 2022. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 509, "MBHBM* Project. II. Molecular Gas Kinematics in the Lenticular Galaxy NGC 3593 Reveal a Supermassive Black Hole"
NASA/ADS
- D. D. Nguyen, M. den Brok, A. C. Seth et al. (incl. T. Tsukui) 2020. The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 892, "The MBHBM* Project. I. Measurement of the Central Black Hole Mass in Spiral Galaxy NGC 3504 Using Molecular Gas Kinematics"
NASA/ADS
- D. D. Nguyen, A. C. Seth, N. Neumayer, et al. (incl. T. Tsukui) 2019. The Astrophysical Journal, Vlo. 872, "Improved Dynamical Constraints on the Masses of the Central Black Holes in Nearby Low-mass Early-type Galactic Nuclei and the First Black Hole Determination for NGC 205"
NASA/ADS
Proceedings
- T. Tsukui, S. Iguchi, I. Mitsuhashi, and K. Tadaki, the Proceedings of the SPIE, Astronomical Telescopes and Instrumentation 2022, Paper Number: 12190-92, "Proper evaluation of spatially correlated noise in interferometric images"
SPIE Digital Library
Codes
- ESSENCE(NASA/ADS):
A python package for evaluating the statistical significance of the image analysis and signal detection under correlated noise in the interferometric images (e.g., ALMA, NOEMA), namely, Evaluating Statistical Significance undEr Noise CorrElation.
- Modified-stardust:
A modified version of the Stardust code (Kokorev et al. 2021, ApJ, 921, 1) to incorporate the spatial decomposition of an image into a point source AGN and an extended host galaxy for galaxy spectral energy distribution modeling. This modified code is described and used in Tsukui et al. 2023, MNRAS, 523, 4654.
Presentations
- Oct. 2025, Galaxy formation group colloqium, CAE Paris-Saclay, Paris, France
- Oct. 2025, ALMA, JWST, Gaia – the Milky Way connection, Paris Observatory, Paris, France
- Sep. 2025, Astronomical Society of Japan Spring meeting, Kaikyo Messe, Yamaguchi, Japan
- Aug. 2025, Hunstead Visitor Workshop New science enabled by Gaia DR4 - the star-gas connection, Wesley College, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
- Aug. 2025, Galaxy Memoirs inferring their past from their present, Armacao dos Buzios, Brazil
- Aug. 2025, 11th Galaxy Evolution Workshop, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan
- Jul. 2025, Tohoku University Colloquium, Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan
- Jun. 2025, Observational Astrophysics (obsap) Seminar, Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan
- May. 2025, International Workshop on Galaxy Formation + AGORA in Asia 2025, Osaka, Japan
- Feb. 2025, Tohoku University Colloquium, Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan
- Feb. 2025, NAOJ Colloquium, National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Tokyo, Japan
- Feb. 2025, Seminar, Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
- Nov. 2024, ANU lunch talk, Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics, ACT, Australia
"The Emergence of Thin And Thick Disks Across Cosmic History"
- Sep. 2024, UNSW, School of Physics colloquium, NSW, Australia
"The Emergence of Thin And Thick Disks Across Cosmic History"
- Aug. 2024, IAU General Assembly, Cape Town, South Africa
"The Emergence of Thin And Thick Disks Across Cosmic History"
- Aug. 2024, IAU General Assembly, Cape Town, South Africa
"Using ALMA as a Thermometer for Host Galaxy Growth of Quasar"
- Jul. 2024, Galaxy evolution colloquium, Oxford University, Oxford, England
"Early Bar-disk Driven Galaxy Transformation at z~4.5"
- Jul. 2024, Special JWST seminar, University Observatory (LMU), Munich, Germany
"Early Bar-disk Driven Galaxy Transformation at z~4.5"
- Jul. 2024, Galaxy coffee, ESO, Garching, Germany
"Early Bar-disk Driven Galaxy Transformation at z~4.5"
- Jul. 2024, EAS Annual Meeting, Padova, Italy
"The Emergence of Thin And Thick Disks Across Cosmic History"
- Jul. 2024, EAS Annual Meeting, Padova, Italy
"Bar-Disk Driven Galaxy Formation in the Cosmic Morning"
- Jun. 2024, ELT Science in Light of JWST, Miyagi, Japan
"The Emergence of Thin And Thick Disks Across Cosmic History"
- Dec. 2023, ALMA/45m/ASTE Users Meeting 2023, Mitaka, Tokyo, Japan
"Galaxy transformation at z~4: insights from spatially resolved 4D (?) ALMA data"
- Nov. 2023, First Star First Galaxy, Sappro, Hokkaido
"Disk-driven galaxy transformation at z=4: insights from spatially resolved ALMA data"
- Oct. 2023, 3D view of galaxies, ASTRO3D online seminar, Canberra, Australia
"Evolution of a barred spiral galaxy at z~4; insights from spatially resolved 4D (?) ALMA data"
- Nov. 2023, The University of Tokyo colloquium, Bunkyo City, Tokyo
"Disk driven galaxy transformation at z∼4: insights from spatially resolved 4D (?) ALMA data"
- Nov. 2023, Lunch talk, Kavli IPMU, Kashiwa, Chiba
"Spatially resolved dust properties and AGN-host decomposition for a starburst galaxy at z~4"
- Nov. 2023, Astrocoffee special talk, NAOJ, Tokyo, Japan
"Disk-driven galaxy transformation at z~4; insights from spatially resolved 4D(?) ALMA data"
- Nov. 2023, Obsap colloquium, Waseda University, Shinjuku, Tokyo
"Spatially resolved dust properties and quasar-galaxy decomposition of HyLIRG at redshift 4.4"
- Aug. 2023, Asia-Pacific Regional IAU Meeting, Fukushima, Japan
"Using ALMA as a thermometer for AGN diagnostics and galaxy evolution"
- Jul. 2023, European Astronomical Society Annual Meeting, Krakow, Poland
"Estimating the statistical uncertainty due to spatially correlated noise in interferometric images"
- Jul. 2023, Galactic bars: driving and decoding galaxy evolution, Granada, Spain
"Bar-driven galaxy evolution at redshift 4.4?"
- May. 2023, New Eyes on the Universe: SKA & ngVLA, Vancouver, Canada
"Estimating the statistical uncertainty due to spatially correlated noise in interferometric images"
- Apr. 2023, The Kavl Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics seminar, Peking, China
"Using ALMA as a thermometer for black hole and galaxy co-evolution"
- Mar. 2023, Bears ALMA Proposal Workshop, Tokyo, Japan
"Spatially resolved ISM properties and AGN-galaxy decomposition of HyLIRG at redshift 4.4"
- Feb. 2023, 9th Galaxy Evolution Workshop, Kyoto Univ. Kyoto, Japan
"Spatially resolved ISM properties and AGN-galaxy decomposition of HyLIRG at redshift 4.4"
- Dec. 2022, ALMA/45m/ASTE Users Meeting 2022, Mitaka, Tokyo, Japan
"Proper evaluation of spatially correlated noise in interferometric images"
- Jul. 2022, SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation Montréal, Québec, Canada
"Proper evaluation of spatially correlated noise in interferometric images"
- Aug. 2022, IAU General Assembly, Koria, Busan
"Spiral disk with concentrated central mass in a Hyper Luminous Infrared Galaxy at a redshift of 4.4"
- Jun. 2022, ASTRO3D galaxy kinematics workshop, Canberra, Australia
"Spiral Galaxies at z=4.4"
- Jun. 2022, 240th Meeting of the American Astronomical Society, Pasadena, California, USA
"Starbursting" disk with a spiral morphology in a Hyper Luminous Infrared Galaxy at redshift of 4.4"
- Mar. 2022, Astronomical Society of Japan, spring meeting
"Internal strucutre of dusty starburst galaxy BRI1335 revealed by ALMA [CII] gas kinematics"
- Sep. 2021, Tsukuba Univ. Theoretical Astrophysics group colloquium, Ibaraki, Japan
"Identifying galactic structures in a galaxy more than 12 billion years ago using the gas dynamics"
- Jun. 2021, Osaka Univ. Theoretical AstroPhysics Group Colloquium, Osaka, Japan
"Rotating gas dynamics and spiral morphology in a galaxy at redshift 4.4"
- Sep. 2019, next-generation VLA workshop, Tokyo, Japan
"HI gas kinematics for SMBH, Bulge and Disk, and Dark matter in the mass assembly history of galaxies"
- Oct. 2019, ALMA2019: Science Results and Cross-Facility Synergies, Sardinia, Italy
"Galactic Dynamics and Dark Matter Profile of NGC1380 with ALMA and VLT/MUSE"
- Jul. 2019, IAUS 353: Galactic Dynamics in the Era of Large Surveys, Shanghai, China
"The measurement of Dark Matter profile of NGC1380 with ALMA and VLT/MUSE"
- Oct. 2018, Armagh Observatory and Planetarium Seminal Talk, Northern Ireland, UK
"Central Black Hole Measurement using Molecular gas dynamics of NGC1380"
Press release
NASA / Tohoku Uni Press release : "NASA's Webb Digs into Structural Origins of Disk Galaxies"
 The figures show how disk formation progresses: early galaxies mainly have a thick disk (bottom), while thin and thick disks often coexist in later galaxies (top). Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, T. Tsukui
The figures show how disk formation progresses: early galaxies mainly have a thick disk (bottom), while thin and thick disks often coexist in later galaxies (top). Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, T. Tsukui
NAOJ Press release : "Discovery of Hot Gas near a Supermassive Black Hole 12.9 Billion Years Ago: New Possibilities for Finding Hidden Black Holes in the Early Universe"
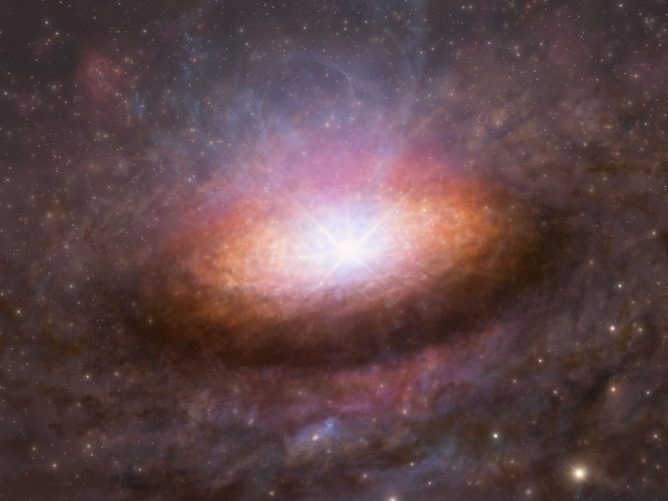 Artist’s illustration based on ALMA data, X-ray radiation from close near a supermassive black hole heats surrounding gas disk, but from the side, visible light and x-rays are blocked by the disk, hiding the commonly used black hole signatures. Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), K. Tadaki et al.
Artist’s illustration based on ALMA data, X-ray radiation from close near a supermassive black hole heats surrounding gas disk, but from the side, visible light and x-rays are blocked by the disk, hiding the commonly used black hole signatures. Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), K. Tadaki et al.
ANU / NAOJ / Kagoshima University Press release : "A Dancing Ancient Galactic Disk at a Peak of Star Formation"
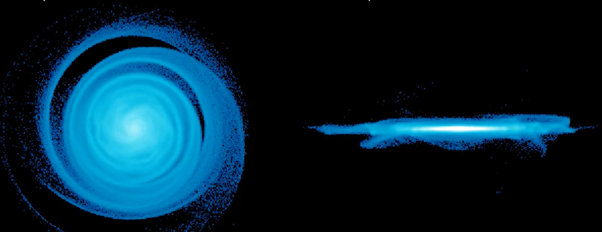 A computer simulation shows a seismic ripple propagating throughout a disturbed galaxy disk, illustrating the observational data well. (Credit: Bland-Hawthorn and Tepper-Garcia, University of Sydney)
A computer simulation shows a seismic ripple propagating throughout a disturbed galaxy disk, illustrating the observational data well. (Credit: Bland-Hawthorn and Tepper-Garcia, University of Sydney)
ASTRO3D Press release : "Heat spot reveal growth rate of a galaxy 12 billion years ago"
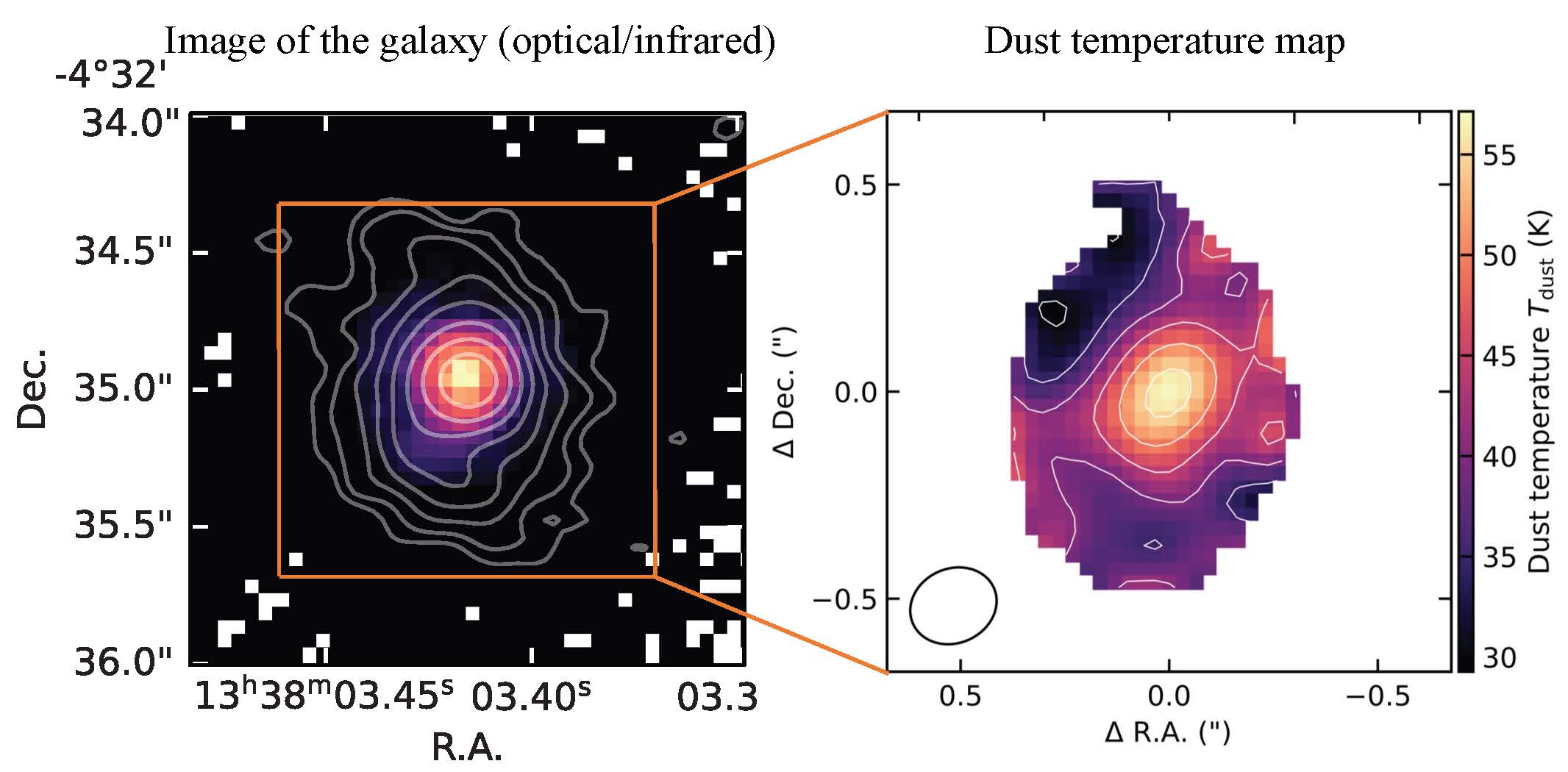 Left: Hubble Space Telescope image showing light from the central suppermassive black hole in BRI 1335-0417. Right: The first dust temperature map of a distant galaxy derived from ALMA observations, revealing the higher temperature near the black hole. (Credit: T. Tsukui)
Left: Hubble Space Telescope image showing light from the central suppermassive black hole in BRI 1335-0417. Right: The first dust temperature map of a distant galaxy derived from ALMA observations, revealing the higher temperature near the black hole. (Credit: T. Tsukui)
SOKENDAI Publication Grant article : "Error analysis method under correlated noise in interferometric images"
 Left: Noise map with a spatial correlation between neighbouring pixels. Right: Noise map without spatial correlation between pixels. Although both noise images have the same amplitude, they look different and affect differently to the uncertainty of the results. (Credit: T. Tsukui)
Left: Noise map with a spatial correlation between neighbouring pixels. Right: Noise map without spatial correlation between pixels. Although both noise images have the same amplitude, they look different and affect differently to the uncertainty of the results. (Credit: T. Tsukui)
NAOJ press release : "ALMA Discovers the Most Ancient Galaxy with Spiral Morphology"
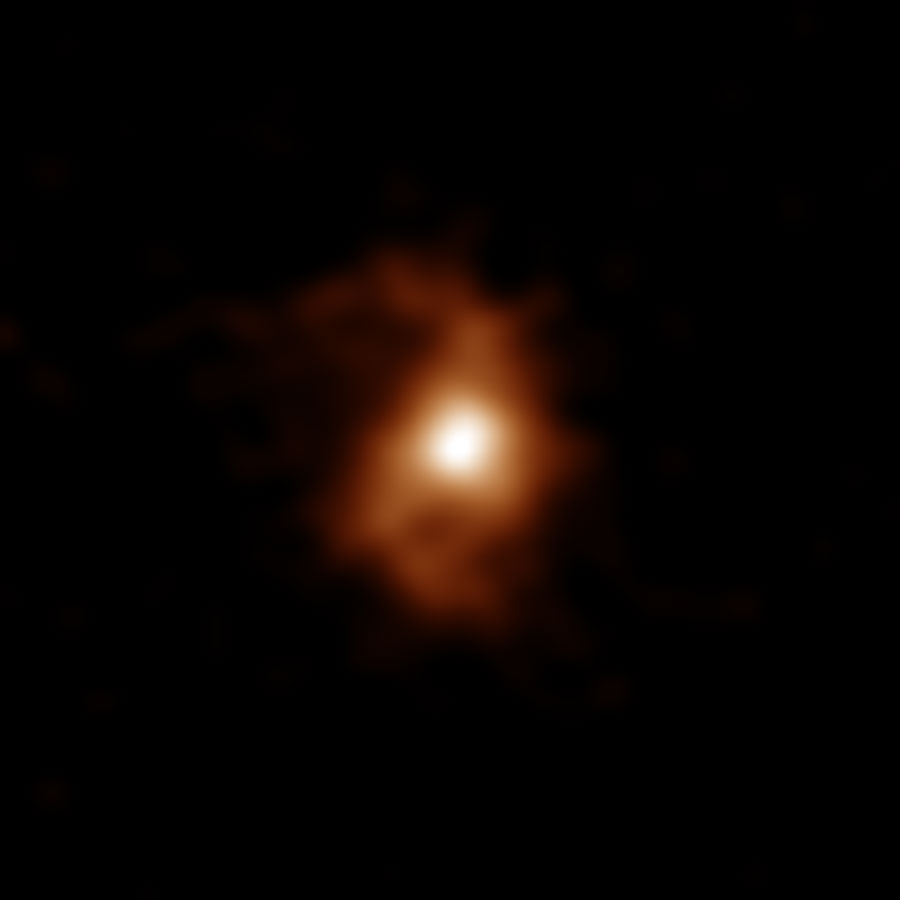 ALMA image of the galaxy BRI 1335-0417 at 12.4 billion years ago. ALMA detected emissions from carbon ions in the galaxy. Spiral arms are visible on both sides of the compact, bright area in the center of the galaxy. (Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), T. Tsukui & S. Iguchi)
ALMA image of the galaxy BRI 1335-0417 at 12.4 billion years ago. ALMA detected emissions from carbon ions in the galaxy. Spiral arms are visible on both sides of the compact, bright area in the center of the galaxy. (Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), T. Tsukui & S. Iguchi)
Contact
Email: tsukuitk23 [at] gmail [dot] com
Adress: Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Mount Stromlo Observatory Cotter Road Weston Creek, ACT 2611 Australia
GithubTwitter
Elements
Text
This is bold and this is strong. This is italic and this is emphasized.
This is superscript text and this is subscript text.
This is underlined and this is code: for (;;) { ... }. Finally, this is a link.
Heading Level 2
Heading Level 3
Heading Level 4
Heading Level 5
Heading Level 6
Blockquote
Fringilla nisl. Donec accumsan interdum nisi, quis tincidunt felis sagittis eget tempus euismod. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus vestibulum. Blandit adipiscing eu felis iaculis volutpat ac adipiscing accumsan faucibus. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus lorem ipsum dolor sit amet nullam adipiscing eu felis.
Preformatted
i = 0;
while (!deck.isInOrder()) {
print 'Iteration ' + i;
deck.shuffle();
i++;
}
print 'It took ' + i + ' iterations to sort the deck.';
Lists
Unordered
- Dolor pulvinar etiam.
- Sagittis adipiscing.
- Felis enim feugiat.
Alternate
- Dolor pulvinar etiam.
- Sagittis adipiscing.
- Felis enim feugiat.
Ordered
- Dolor pulvinar etiam.
- Etiam vel felis viverra.
- Felis enim feugiat.
- Dolor pulvinar etiam.
- Etiam vel felis lorem.
- Felis enim et feugiat.
Icons
Actions
Table
Default
| Name |
Description |
Price |
| Item One |
Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. |
29.99 |
| Item Two |
Vis ac commodo adipiscing arcu aliquet. |
19.99 |
| Item Three |
Morbi faucibus arcu accumsan lorem. |
29.99 |
| Item Four |
Vitae integer tempus condimentum. |
19.99 |
| Item Five |
Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. |
29.99 |
|
100.00 |
Alternate
| Name |
Description |
Price |
| Item One |
Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. |
29.99 |
| Item Two |
Vis ac commodo adipiscing arcu aliquet. |
19.99 |
| Item Three |
Morbi faucibus arcu accumsan lorem. |
29.99 |
| Item Four |
Vitae integer tempus condimentum. |
19.99 |
| Item Five |
Ante turpis integer aliquet porttitor. |
29.99 |
|
100.00 |







